Cockroach morphology
Click on the following link for the ppt download
CLASSIFICATION OF COCKROACH

• PHYLUM: Arthropoda
• ORDER: Blattodea
• GENUS: Periplaneta
• SPECIES: americana
Features Of Cockroach
•Cockroaches are brown or black bodied animals.
• Bright yellow. red and green-colored cockroaches have also been reported in tropical regions.
• Their size ranges from 1/4 inch to 3 inches (0.6 -7.6 cm) and has long antennae. legs and a flat extension of the upper body wall that conceals the head.
• They are nocturnal omnivores that live in damp places throughout the world.
•They are serious pests and vectors of several diseases.
•(Cockroaches are nocturnal omnivore means they are active at night and they can eat both plant and animal products)
- The morphology of Periplaneta americana is about 34- 53 mm long with wings that extend beyond the tip of the abdomen in males.
- Its body is divided into the head, thorax, and abdomen.
- The entire body is covered by a hard chitinous exoskeleton.
- The exoskeleton has hardened plates called sclerites that are joined to each other by a thin and flexible articular membrane
- Sclerites are classified as tergum/tergites for the dorsal side & Sternum/sternites for the ventral side
Head
•It is pear-shaped and six-segmented.
• It lies at a right angle to the body with the broad side upwards.
• It articulates with the thorax by the flexible neck. On each side of the head is a large compound eye.
• They have a pair of antennae articulate in pits close to the notches of the compound eyes.
• The top of the head is termed a vertex.
• Antennae have sensory receptors that help in monitoring the environment.
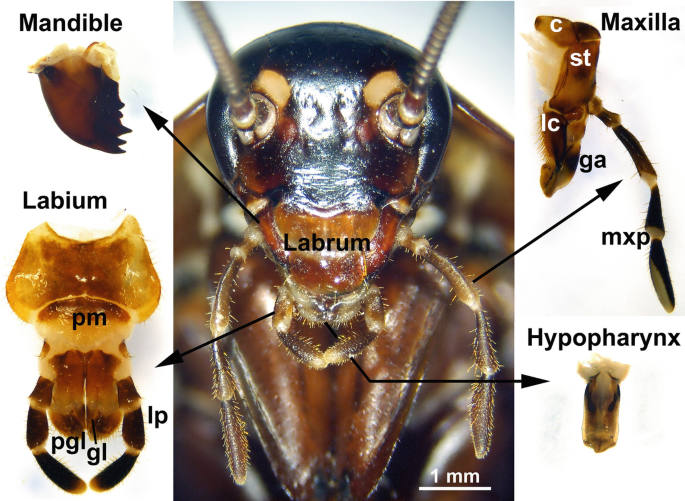
•Mouth parts are of biting & chewing type, surrounded by 5 kinds of appendages
• These include the labrum (upper lips ), mandibles, first maxillae,
second maxillae Labium ( lower lips) and hypopharynx ( tongue)
second maxillae Labium ( lower lips) and hypopharynx ( tongue)
Labrum
a simple plate-like sclerite that serves as a front lip to help contain the food
Mandibles
a pair of jaws for crushing or grinding the food. They operate from side to side, not up and down.
Maxillae
to hold and manipulate food so that it can be chewed or sliced by the mandibles.
Hypopharynx
a tongue-like process that helps mix food and saliva
Labium
helps hold food in place when the insect feeds
Thorax
•The thorax consists of three segments Prothorax, Mesothorax, and Metathorax.
• The head is connected to the thorax by a short extension of the prothorax known as the neck.
• Each thoracic segment bears a pair of walking legs.
• The first pair of wings arise from mesothorax and the second pair from metathorax.
• Forewings called tegmina are opaque dark and leathery and cover the hind wings when at rest.
• The hind wings are transparent, and membranous, and are used in flight.
Abdomen
- In both males and females abdomen consists of 10 segments.
- In females, the 7th sternum is boat-shaped and together with the 8th and 9th sterna form a brood or genital pouch whose anterior part contains female gonopore, spermathecal pores, and collateral glands.
- In males, the genital pouch or chamber lies at the hind end of the abdomen bounded dorsally by the 9th and 10th terga and ventrally by the 9" sternum.
- It contains a dorsal anus, ventral male genital pore, and gonapophysis. Males bear a pair of short, thread-like anal styles which is absent in females.
- In both sexes, the 10th segment bears a pair of jointed filamentous structures called anal cerci.
Digestive System
• Alimentary canal is divided into three regions ; foregut, midgut, and hindgut.
• The mouth opens into short pharynx leading to the esophagus .
• Oesophagus opens into a sac like crop, which stores food.
• Crop is followed by gizzard or proventriculus.
• Gizzard contains 6 chitinous teeth for grinding the food
• Outer layer has circular muscles.
• The entire foregut is lined by cuticle.
• A ring of 6- 8 blind tubules called hepatic or gastric caecae present at the junction of foregut and midgut,
which secretes digestive juices. (fats carbohydrates and protein digestion.)
• Midgut is a long tube like structure.
Secretes peritrophic membrane
• At the junction of midgut and hindgut,
another ring of 100 -150 yellow-colored thin filamentous malpighian tubules are present.
• Malpighian tubules are meant for excretion from the hemolymph.
• The hindgut is broader and differentiated into Ileum, colon, and rectum
Blood Vascular System
• Blood vascular system is open type
• Blood vessels are poorly developed and
open into space called the hemocoel
• Visceral organs located in the
hemocoel and bathed in the blood called hemolymph
• The hemolymph is composed
of colorless plasma and hemocytes
• The heart is elongated 13 chambered,
funnel-shaped with Ostia [49beats/min]
• Blood enters the heart through
Ostia (guarded by valves) and is pumped anteriorly into the sinuses.
• The hemocoel differentiated into three
sinuses:
Pericardial sinus.
Perivisceral sinus
Perineural sinus
Respiratory System
• The respiratory system consists
of a network of the trachea
• Trachea opens to the outside by 10 pairs of smallholes called spiracles on the the lateral side of the body.
• Trachea gives rise to branching tubes called tracheal tubes which are subdivided into tracheoles
• Opening of spiracles regulated by valves.
• Ventilation of the tracheal system is by alternate contraction and relaxation of abdominal muscles (Tergo-sternal) muscles
• Movement of air takes place by diffusion and directly to the body cell.
Excretion
• Excretion is performed by malpighian tubules. (Present between midgut & hind gut)
• Each tubule is lined by glandular and ciliated cells.
• They absorb nitrogenous wastes from the hemocoel, convert them into uric acid, and pour them into the hindgut.
• Hence cockroach is uricotelic in nature.
• Nephrocytes ( lateral walls of the heart), fat bodies, and uricose glands also assist in excretion.
Nervous System
• Consists of a series of segmentally arranged ganglia joined by paired longitudinal double ventral nerve cords
• Three ganglia lie in the thorax and six in the abdomen
• The head contains a bit of the nervous system.
• The brain is represented by supra oesophageal ganglion which innervates the compound eye and antennae.
• The sense organs are antennae, eyes maxillary palps, labial palps, anal cerci,
• Each compound eye consists of about 2000 hexagonal ommatidia
• Each ommatidium forms a part of the image, called mosaic vision
There are two types of vision in insects – mosaic vision (or apposition image) during the daytime and
superposition (or dull image) in dim light.
- Sense organs in cockroaches are – photoreceptors (compound and simple eye),
- thigmoreceptors (antennae),
- chemoreceptors (on maxillary and labial palps, labium and hypopharynx) and auditory receptors on anal cerci.
Reproductive System
• Cockroaches are dioecious and sex organs are well developed.
• The male reproductive system consists of a pair of testes lying one on each side from the 4 th to 6 th segments.
• Vas deferens arise from each testis and open into the ejaculatory duct through the seminal vesicle
• The ejaculatory duct opens into the male gonopore situated ventral to the anus.
• The accessory reproductive gland, the mushroom gland, is present in the 6th 7th segment.
• External genitalia are represented by male gonapophysis or phallomere
• Sperms are sorted in the seminal vesicles and glued together in bundles called spermatophores, which are discharged during copulation.
• Phallic gland secretes the outermost layer
•The female reproductive system consists of two large ovaries present in the 2nd 6th abdominal segments.
• Each ovary has formed a group of eight ovarian tubules or ovarioles, containing a chain of developing ova.
• Oviduct of each ovary fused to form a single median oviduct or vagina, which opens into the genital chamber
• A pair of spermatheca is present in the 6th segment which opens into the genital chamber.
• Sperms are transferred through spermatophores.
• The fertilized eggs are encased in capsules called oothecae
• The ootheca is a dark reddish to blackish brown capsule about 3/8" long.
• On average, females produce 9-10 oothecae each containing 14-16 eggs
•Development is paurometabolous i.e development through nymphal stages.
• The nymph grows by moulting about 13 times to reach the adult form.


Comments
Post a Comment